Ectopic pregnancies are a condition that happens in pregnant women when the egg does not grow in the correct place in the abdomen. Due to modern advancements in medicine, ectopic pregnancies have increased but the mortality rate has decreased significantly in part due to better availability of surgery and other treatments. In the 19th century, before many modern medical advancements, the death rate from ectopic pregnancies was over 50%. Near the end of the 19th century and beginning of the 20th century, strides were made in the treatment of ectopic pregnancies and the death rate dropped to below 5%.
One thing that has remained the same since the 19th century is that the main reason for deaths from this type of pregnancy issue is caused by the failure to detect the problem or women not noticing the abnormalities that occur with it. Ectopic pregnancies are still the top cause of pregnancy related deaths during the first trimester. Interestingly, the rate of ectopic pregnancy is increasing in modern times. Advanced treatments including shots and surgery are dramatically improving the outcomes for millions of fertile women.
This article will cover the facts about ectopic pregnancy, as well as risks, and most importantly the most common symptoms that you’ll want to pay special attention to.
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
“Ectopic pregnancy” is the name of the condition that happens when a woman’s fertilized egg locates itself outside of the inner uterus lining and starts growing there. Most ectopic pregnancies happen in the fallopian tubal area. Medical studies estimate about 98% of diagnosed ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tube. They are also called tubal pregnancies. The fertilized egg can also settle in other places, which is much less common, such as the cervix, abdominal cavity and ovaries. Current estimates put the rate of ectopic pregnancy is at about 1 in 50 pregnancies.
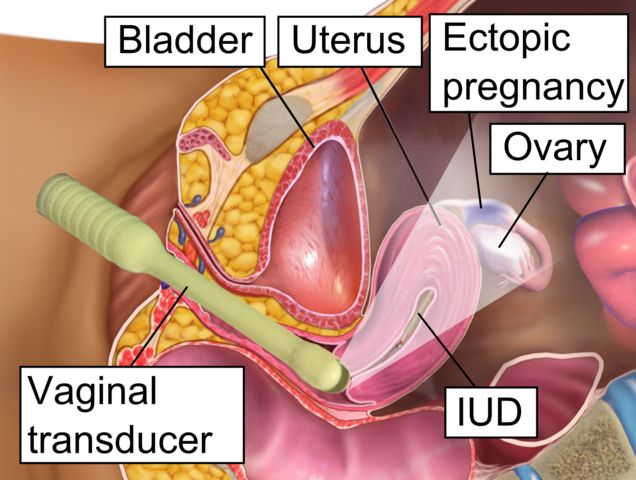
Author: Mikael Häggström, wikimedia
Ectopic Pregnancy Risks
The most common risk of an ectopic pregnancy for a woman is internal bleeding. Some women with an undiagnosed ectopic pregnancy, who also don’t realize they are pregnant, start off with bleeding that they may attribute incorrectly to their period starting. However, the bleeding from this type of pregnancy may not stop. It is typically because of a rupture of the fallopian tube. Fainting or sudden collapse from the loss of blood can occur. In addition to bleeding, there is the risk that the internal blood will result in scar tissue formation, which can affect future pregnancies in terms of fertility and problems that may occur.
Interestingly, some women can have an ectopic pregnancy and experience few or no symptoms and have no detrimental effects. Basically, the pregnancy is absorbed into the system and resolves itself. In these cases, no treatment is needed but careful medical observation is recommended.
Most Common Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
The most common symptoms include abdominal pain, lack of menstrual periods and vaginal bleeding. Bleeding is usually intermittent, and causes many women to mistake it for their periods. If a woman knows she is pregnant, and experiences any amount of vaginal bleeding, it is critical to get medical attention right away. Early treatment is critical for a good outcome to occur with this condition.
The pain, bleeding and lack of menstruation can occur when the pregnancy has ruptured and also if it has not ruptured. Medical attention is extremely critical also because these symptoms while pregnant can also be attributed to other conditions, such as a miscarriage. It is critical to get a proper diagnosis as soon as possible.
The timeline of ectopic pregnancy symptoms is also critical to notice. An ectopic pregnancy will typically start displaying symptoms between 6 and 8 weeks after your last period. However, if the pregnancy did not begin in the fallopian tube, but somewhere else, such as the cervix, ovary or abdominal cavity, then these symptoms may not be noticeable until later in the pregnancy.
More Signs and Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Here is a more detailed list of symptoms that can happen with this condition:
Additional symptoms that can happen and are critical to get medical attention for include:
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Low blood pressure
- Shock
- Weak or rapid pulse
- Pale skin
- Confusion
- Fainting
- Rectal pain
- Shoulder pain



